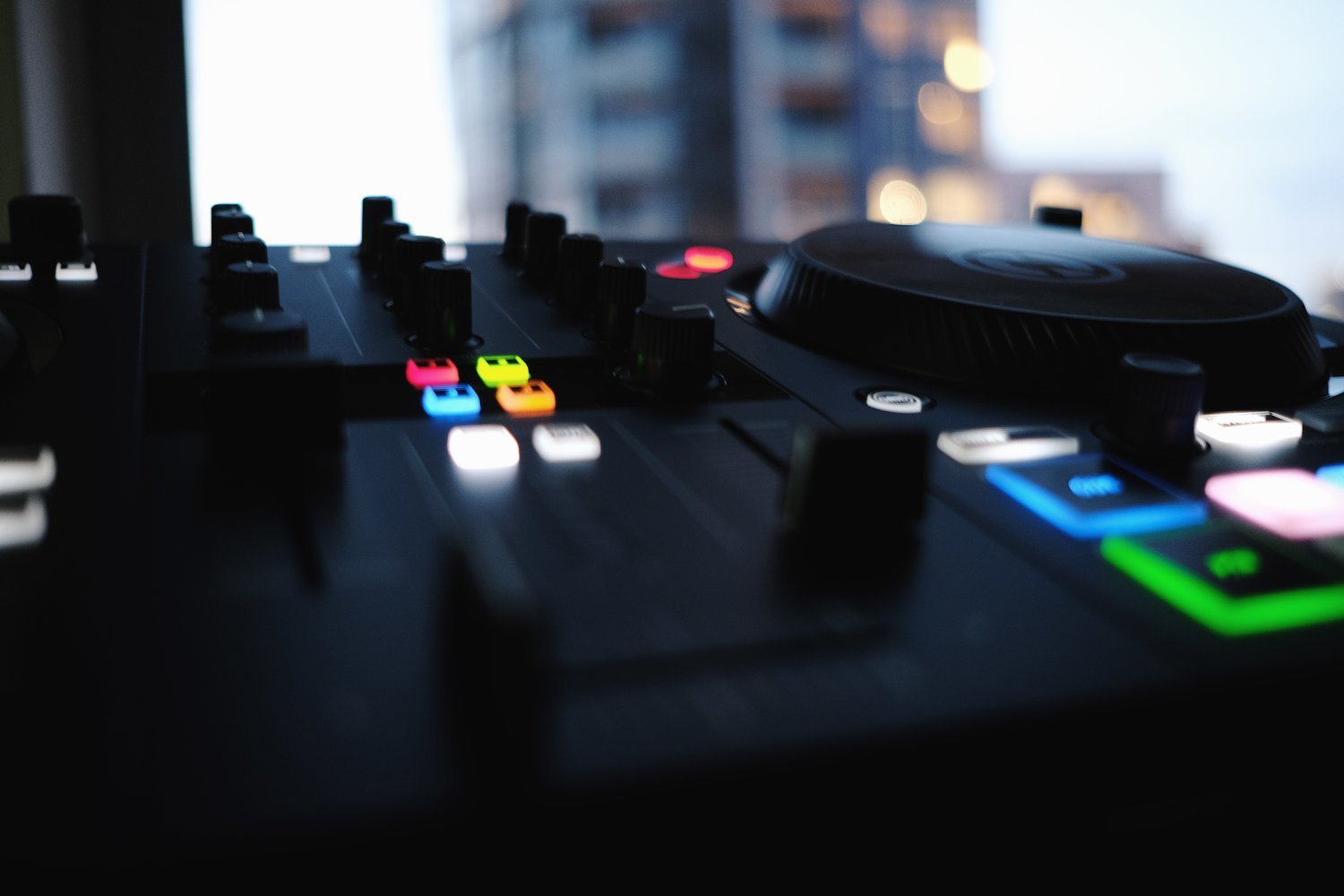
DJing has come a long way from its humble beginnings. What started as a simple act of playing records has transformed into a complex, multifaceted art form. Over the decades, the evolution of DJing has been shaped by technological advancements, cultural shifts, and changes in musical genres. In this post, we’ll explore the key milestones in the evolution of DJing, from vinyl to digital, and how these changes have impacted the industry.

The Birth of DJing: The 1940s to 1960s
The origins of DJing can be traced back to the 1940s and 1950s, when radio DJs first began to play music on the airwaves. These early pioneers were responsible for selecting and presenting music to listeners, often without mixing or blending tracks. They played a crucial role in popularizing new music and shaping the music industry.
The Rise of Vinyl Records
In the 1960s, the introduction of vinyl records and turntables revolutionized DJing. DJs like Francis Grasso and Kool Herc began experimenting with mixing records, using two turntables to create seamless transitions between songs. This marked the first step towards live mixing, setting the stage for the vibrant club scenes that would emerge in the following decades.
The Disco Era: 1970s
The 1970s saw the explosion of disco music and the rise of the club scene. This era was pivotal in shaping modern DJing, as DJs began to use mixing techniques to create continuous music for dancers.
The Emergence of the Turntable as an Instrument
During the disco era, DJs were no longer just playing songs—they were creating an experience. DJs like Larry Levan and David Mancuso were known for their ability to manipulate records and create unique mixes that kept the energy high on the dance floor. The turntable itself became an instrument, with DJs using cueing, scratching, and beatmatching to extend tracks and keep the groove going.
The Introduction of DJ Equipment
The development of the SL-1200 turntable by Technics in the mid-1970s marked a significant technological advancement. The turntable became the standard in DJing, thanks to its durability, precision, and ability to adjust pitch, giving DJs more control over their mixes.
The Rise of Hip-Hop and Turntablism: 1980s
The 1980s brought about the birth of hip-hop and the evolution of turntablism. As hip-hop culture took hold, DJs played an even more significant role in shaping music and culture.
The Birth of Turntablism
In the 1980s, DJs like Grandmaster Flash and Jam Master Jay pushed the boundaries of what could be done with turntables. They introduced techniques like scratching and backspinning, which became signature elements of hip-hop DJing. These DJs were no longer just playing music—they were crafting unique sounds, making them the true innovators of modern DJ culture.
The Growth of the Underground Scene
During this time, underground club scenes flourished, and DJs became the central figures in these communities. The rise of hip-hop and electronic music led to the growth of underground parties and raves, where DJs played an essential role in setting the tone and maintaining the vibe of these events.
The Digital Revolution: 1990s to Early 2000s
The 1990s marked a significant shift in DJing, as technology advanced and digital tools began to change the landscape of live performance.
The Shift to Digital Equipment
The introduction of CDJs and laptops transformed the way DJs performed. The CDJ allowed DJs to play digital tracks from CDs, replacing the traditional vinyl setup. This made DJing more accessible and efficient, as DJs could carry hundreds of tracks in a small device rather than hauling around crates of vinyl records.
Software and Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs)
With the rise of programs like Traktor and Serato, digital DJing became even more versatile. These software platforms allowed DJs to mix and manipulate tracks with greater precision, using features like automatic beatmatching and looping. The use of digital audio workstations (DAWs) like Ableton Live also gave DJs more freedom to produce and perform their own original tracks during live sets, blurring the lines between DJing and music production.
The Modern Era: 2010s to Present
The 2010s ushered in a new era of DJing, where digital tools, social media, and live streaming have transformed the industry into a global phenomenon.
The Popularity of DJ Culture
As EDM (electronic dance music) exploded in popularity, DJs like David Guetta, Calvin Harris, and Avicii became international superstars. DJing was no longer just a niche hobby—it became mainstream. Festivals like Tomorrowland and Ultra Music Festival attracted hundreds of thousands of fans, and DJing became a global cultural force.
The Rise of Streaming and Live Streaming
With the rise of streaming platforms like Spotify and SoundCloud, DJs now have instant access to an almost infinite library of tracks. In addition, live streaming services like Twitch and YouTube have allowed DJs to reach audiences worldwide, performing in front of global audiences without leaving their homes.
Controller-Based DJing and Software Integration
Modern DJs now use DJ controllers that combine the functionality of traditional turntables with the power of digital software. These controllers often come equipped with features like touch-sensitive jog wheels, built-in soundcards, and multi-channel mixing capabilities. This integration of hardware and software makes it easier for DJs to manipulate tracks in real-time, without needing bulky equipment.
Conclusion: The Future of DJing
The evolution of DJing has been shaped by technological advancements, cultural shifts, and the creativity of the artists themselves. From the early days of radio to today’s high-tech digital setups, DJing has grown into a powerful form of musical expression. As technology continues to evolve, the role of the DJ will likely continue to expand. With the rise of AI, virtual reality performances, and new software tools, the future of DJing looks more exciting than ever. The key, however, remains the same: the DJ’s ability to connect with the crowd, read the room, and create unforgettable experiences through music.